Intellectual property rights are like some other property rights that provide permissions to owner, creator, and inventor to make a profit by their own work or interest in creation through licenses, patents, trademarks, and copyrighted documents. These rights are sketched out in Article 27 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, which gives the option to profit by the insurance of good and material of interests resulting from the creation of logic, scholar, and masterful creations. The significance of scholarly property was first perceived in the Paris Convention for the Insurance of Industrial Property (1883) and the Berne Convention for the Protection of Literary and Imaginative Works (1886). Both the bargains are directed by the World Intellectual Property Association (WIPO). Intellectual property rights are the rights given to people over the manifestations of their brains and provide the inventor an exclusive right over the utilization of his/her invention for a specific time period.
Development of Intellectual Property Law in India
Protected innovation Right (IPR) in India was imported from the west. The Indian Trade and Merchandise Marks Act 1884, was the main Indian Law with respect to an IPR. The law on patents in Indian was sanctioned in 1856 followed by a progression of Acts being passed. The Indian Patents and Designs Act in 1911 and the Indian Copyright Act in 1914 had sanctioned. Indian Trade, Merchandise Marks Act, and Indian Copyright Act have been changed by the Trade and Merchandise Marks Act 1958 and Copyright Act 1957 individually.
In 1948, the Indian Government selected the first board of trustees to survey the overall Patents and Design law. In 1957, the Government established a Justice Rajagobala Ayyangar Committee (RAC) to revise the Patent Law. Rajagobala Ayyangar Committee presented its first report in the year 1959, the report tried to adjust the established assurance of financial and social equity cherished in the preface of the constitution. This report gave the procedure to the Patenting of medications and medical drugs. This report laid out the approach behind the Indian Patent system.
The theory on which the patent system depends on, i.e., a chance of securing elite rights in development, inventions and creation are specialized procedure in four different ways.
1. Supports exploration and innovation.
2. Initiates a designer to unveil his designs.
3. Offers grant for the costs of innovations.
4. Gives a prompting to put capital in new lines of innovation which probably won’t seem beneficial.
In view of the Rajagobala Ayyangar Committee report, a Bill was presented in the year 1965 and the bill was passed in the Lok Sabha however it lapsed in the Rajya Sabha and again lapsed in Lok Sabha in the year 1966 because of the disintegration of Lok Sabha. In any case, it was reintroduced in 1967 and went in 1970; the draft rules were consolidated in Patent Act and passed in the year 1971. The accompanying advances are being recommended with specific reference to the circumstance in India in regards to IPR in the national strategy making.
Establish a coordinated single window National IPR commission to manage IPR strategy issues;
- Integrate national innovation arranging with IPR and patterns in global innovation exchange;
- Implement a conventional national IPR education crucial;
- Set-up IPR preparing organizations to get ready actually qualified lawyers;
- Introduce an empowering national tax assessment strategy to energize advancement, working of IPR portfolio and its use in innovation move and exchange;
- Urgently modernize the IPR authoritative structures in the nation;
- Improve the system forget to and successful utilization of IPR data. There is a pressing need to blend the patent characterization system to ease and enhance forms in patent looking;
- Re-structure the legal executive and requirement hardware for expert and expedient reaction to IPR issues;
- Training of corporate and institutional chiefs on viable administration of IPR;
- Standardize models for valuation and review of IPR;
- Evolve national tax assessment policies of improvement, use, and exchanges connected to IPR.
Evaluation of an International Intellectual Property System
The establishment of International Intellectual Property Protection was made in the nineteenth century at different Congresses in Vienna and the remainder of Europe. The assurance of Industrial Property was made in Paris Convention in the year 1883. Licenses, Trade Marks and Industrial plans were the three primary properties that were conceded security in this show. In 1998, India turned into an individual from the Paris Convention. The establishment of International Intellectual Property Protection was made in the nineteenth century at different Congresses in Vienna and the remainder of Europe. The assurance of Industrial Property was made in Paris Convention in the year 1883. Licenses, Trade Marks and Industrial plans were the three primary properties that were conceded security in this show. In 1998, India turned into an individual from the Paris Convention.
In 1886, International Copyright Act was passed (bringing about the encircling of the Berne Convention for the assurance of scholarly and aesthetic works). The Paris Convention denoted the start of the International Trade Marks Protection laws and presented the idea of a notable imprint. Extraordinary associations and game plans have been made for the nations who are individuals from the Paris Convention. Madrid understanding is one exceptional game plan that was made to normalize the trademarks. Madrid understanding exemplifies the basic standards delineated in the Paris Convention.
The importance of intellectual property in India is entrenched at all levels-legal, regulatory and legal. India sanctioned the understanding setting up the World Trade Organization (WTO). This Agreement, intra-alia, contains an Agreement on Trade Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) which came into power from first January 1995. It sets out the base principles for security and authorization of licensed innovation rights in part nations which are required to advance viable and sufficient insurance of protected innovation rights with the end goal of lessening mutilations and hindrances to worldwide exchange. The commitments under the TRIPS Agreement identify with arrangement of least principles of insurance inside the part nations lawful frameworks and practices. The IPR scene in India has experienced a sensational change since 1995 with the formation of different instruments of Intellectual Property.
IPR is as of now a piece of the key choices in the information business. So as to guarantee continued development, upgraded benefits and market administration, numerous enterprises have structured their venture the executives system for
- Optimized utilization of inter/intra information base.
- Strategic administration of IPR.
- External channels for information and creations as sources of info.
- Internal aptitude to oversee exploration and coordinated efforts.
- Clarity on information proprietorship issues through commonly gainful licenses.
- Pooling of IPR as on account of a few organizations that have framed patent pools of their licenses for shared advantages
The rising scene later on will look for positive linkages between improving rivalry in the public eye on one hand and setting up lawful responsibility for on the other. Unequally between weaved cultural, good and moral issues are previously impacting ways to deal with universal exchange including innovation the executives, responsibility for and business forms.
New Dimensions and Issues for Resolution of intellectual property
As innovation investigates more up to date measurements and unknown ways in the coming decades, IPR will expect favourable structures to support advancement and information partaking in a serious system. The interlaced issues in IPR such as:
- Domain names and trademarks: Copyright in the internet.
- Rights on customary information, earlier workmanship, material exchange understanding and bio-prospecting.
- Software and patents
- Biotechnological developments and good issues and patents.
- Compulsory permitting alternatives, outskirt measures and equal imports and depletion of IPR.
- Government control on fare of innovation.
Effect of stronger IPR in developing nations
Society receives the accompanying four benefits from allowing such restraining infrastructure rights to inventions:
- The incitement of new inventions by private specialists, the essential social advantages of IPR.
- The utilization of new information in beneficial activity.
- The more prominent dispersal of new information to different operators.
- The incitement of inventions and innovation by different undertakings.
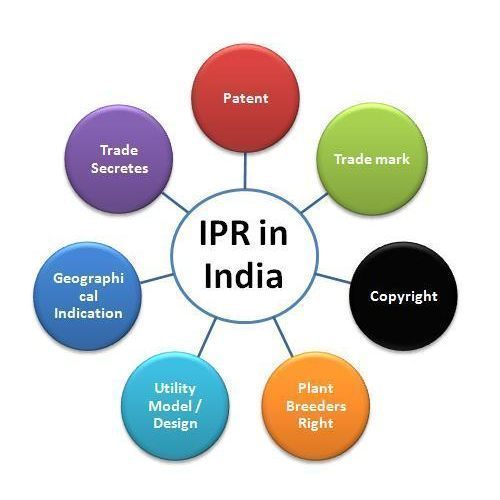
The TRIPS Agreement accommodates standards and principles in regard of following territories of intellectual property
- Patents
- Copyrights and related rights
- Trade Marks
- Geographical Indications
- Trade Marks
- Layout diagram of Integrated Circuits
- Industrial Designs
- Trade Secrets
- Varieties of plants.
Significance of IPR in developing nations
There has been at time impressive discussion on the effect on developing nations of fixing Intellectual Property Rights. The possible importance of IPR in developing nations is as indicated by the overall force of their mechanical movement. Creating nations obliged the TRIPS understanding for an assortment of reasons, extending from the desire for extra access to rural and clothing markets in rich countries, to a desire that more grounded IPR would support extra innovation move and development. In any case, the promising long haul benefits are questionable and exorbitant to accomplish in numerous countries, particularly in the least fortunate nations. There are motivations to accept that the authorization of IPRs positively affects development possibilities. On the residential level, development is encouraged by more elevated level of advancements in spite of the fact that this outcome will in general be genuinely inconsequential until nations move into the centre level of pay. It additionally takes note of that the development impacts of IPRs are at various occasions and in various locales of the world, nations have acknowledged high paces of development under shifting degrees of IPR assurance. There are unquestionably momentary expenses for poor nations from stronger IPRs, as more significant expenses for innovation , invention and secured items.
Conclusion
IPR are considered to accomplish financial, social and technical headway that secures the thoughts and innovative development, designs and helps to the production of inventions. The different kinds of IPR were intended to give the proper ownership of responsibility for information with advantages sharing between proprietors in development to make a specialty of themselves. It likewise prompts creation. The capacity of IPR system is additionally to encourage the exchange of innovation as joint endeavours and permitting. The social reason for IPR is to give insurance to the after effects of interest in the improvement of new innovation, in this way giving the motivating force and methods for fund for additional innovative work of information base; while fundamental social target of IPR assurance is that the selective rights given to the inventor, focused on adjusting the parity that must be framed between the authentic interests of rights holders.